In this introduction to eCommerce, we outline what this means, what you can sell, and what platforms you can use. It refers to the activity of buying or selling products or services over the internet. This is a hugely broad definition and includes anyone conducting commercial transactions online. It’s important to break this down a bit further to the types of eCommerce businesses that exist and whom they sell to.
Types of eCommerce businesses
It’s possible to categorise eCommerce businesses into four main types of activity.
- Physical products
- Digital products
- Services
- Affiliates
Physical products
eCommerce stores selling physical products are the type that first comes to mind. These are tangible items that you can touch, feel and hold. They’ll need to be shipped and packaged, often to many countries around the world. This includes the added complexity of storage, postage rates, delivery companies and dealing with physical returns among many other aspects.
Digital products
Digital products are files sent to a customer, usually immediately, and are most often accessible right away without any physical shipping process needing to be undertaken. An example of this is the Shoptimizer WooCommerce theme we sell on this very site. Once purchased, you get a download link within seconds.
Services
Services can be anything from business consulting to driving lessons sold online, often by the hour. We’re seeing more and more seemingly traditional occupations offering ways to book and buy online.
Affiliates
Affiliates refer to websites marketing or selling other businesses products for a percentage cut from each sale. These kind of sites don’t need to actually hold any stock themselves, they simply act as a conduit for others.
They can include review sites such as the New York Times owned Wirecutter or indeed huge marketplaces like Etsy. The whole area of dropshipping which we’ll cover in more detail later would come under this categorization also.
Who can I sell to?
Technically, anyone. But most eCommerce sites break down their customers into three main strands.
- B2C – Business to consumer. These eCommerce companies sell physical or digital products to the end consumer.
- B2B – Business to business. These can include manufacturers that supply raw materials to other businesses.
- B2G – Business to government. In most countries the government is a huge employer with their own specific set of requirements. They include everything from IT systems to uniforms and food. A B2G enterprise focuses on this.
Now you might think that B2C is the biggest of these three by market share. Well, it’s actually dwarfed by B2B. Research from Statista in 2019 found that the global market size was as follows for 2018.
What eCommerce platforms are there?
There are a lot. Just some of the eCommerce options you have includes Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, BigCommerce, SquareSpace, Wix, OpenCart, PrestaShop, Volusion, BigCartel, Ecwid, Foxy, and Zen Cart.
In terms of popularity, statistics from BuiltWith give an estimate by analyzing the top million eCommerce sites.
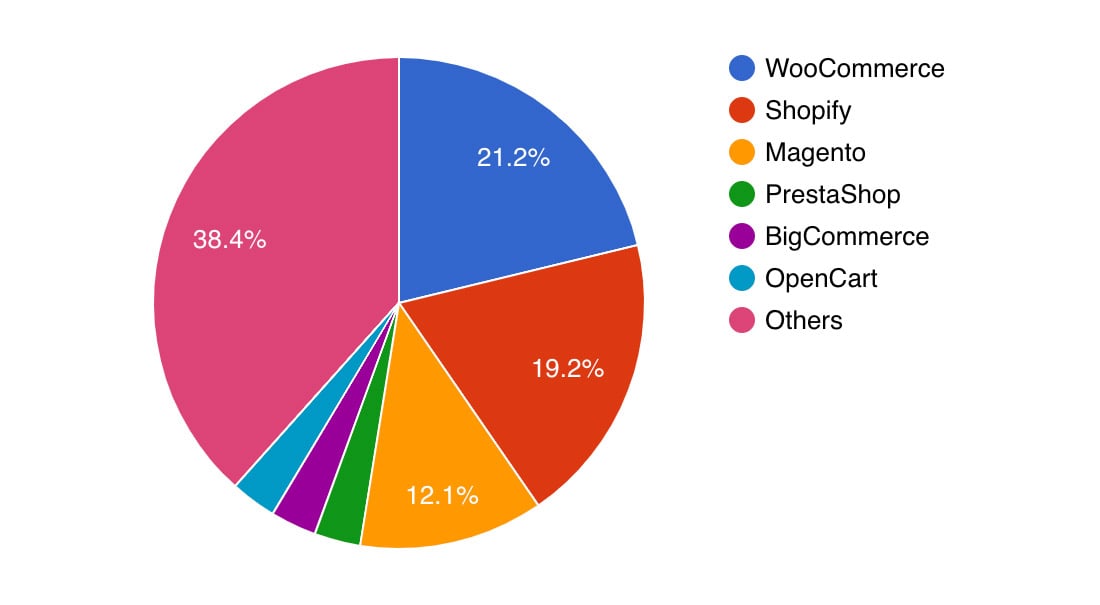
The top platforms in order are WooCommerce, Shopify and Magento, with the rest of the competition quite a distance behind. These numbers may not tell the whole story however so let’s also look at Google Trends to see what people are searching for.
For worldwide searches for the past five years, Shopify began to overtake WooCommerce in early 2016 and has continued this trajectory. Magento, once the dominant platform, has steadily declined and is now close to parity with WooCommerce.
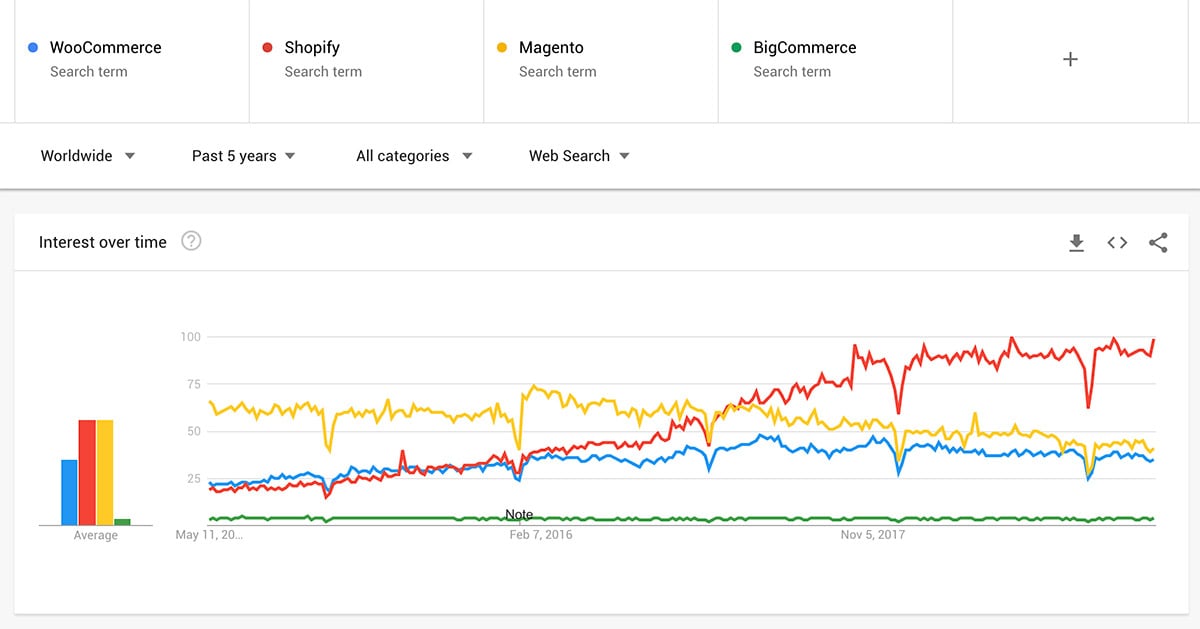
When we look at the data by region, Shopify is vastly more popular in wealthy countries where eCommerce is very much established as a buying medium. In the United States, when comparing these big four platforms, 58% of searches are for Shopify and 16% for WooCommerce.
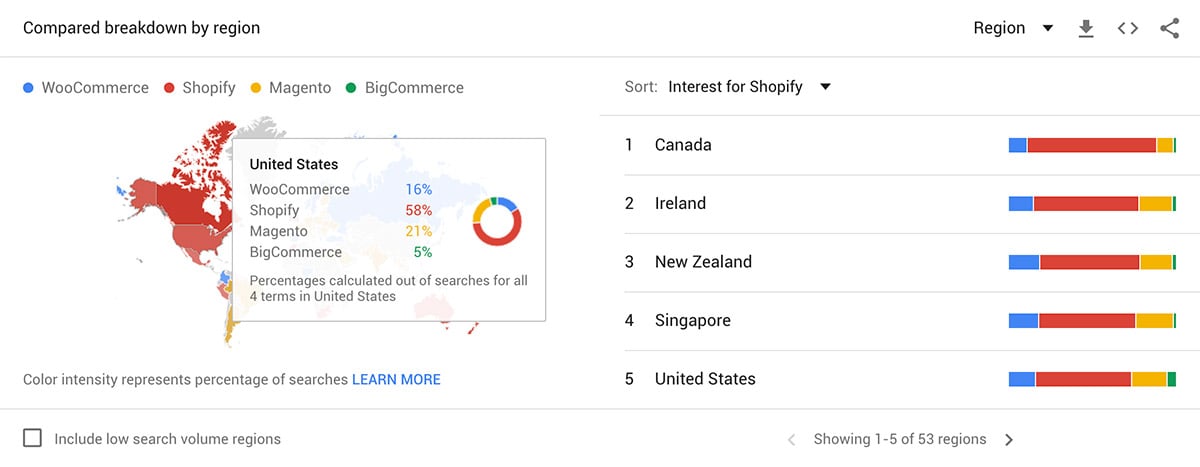
It’s important to take these trends not too literally. Remember, they refer only to search volumes for each term. They don’t include active installs or the number or orders processed by each platform.
Nonetheless, they provide a useful snapshot into what users are searching for when deciding on which eCommerce platform to choose. The decline of Magento search volume and rise of Shopify does mirror the data provided by BuiltWith.
Shopify
Shopify is an extremely well-rounded eCommerce platform, and is very easy to setup and use due to its simple on-boarding process and excellent dashboard. It has an excellent selection of professional looking themes to choose from, albeit on the pricey side, with many around $180.
It’s ideal for small to medium-sized stores and for people starting eCommerce businesses who don’t have an existing site. However, for larger stores, the monthly costs for additional apps and the transaction fees can become sizeable.
Shopify Pros
- The easiest eCommerce platform to start with, especially if you don’t have an existing site.
- Hosting and uptime all taken care of, you won’t need to manage this yourself. You can focus on selling and marketing your products.
- 24/7 customer support including phone, email, and live chat. This is ideal for people starting off and who aren’t especially technically minded.
Shopify Cons
- Although the headline price of $29 a month seems reasonable this quickly climbs when you add additional features and apps. Shopify also takes a percentage cut from each sale which can add up if you sell in large volumes.
- Lacks WooCommerce’s capabilities when it comes to SEO and all round flexibility.
WooCommerce
WooCommerce is the most popular eCommerce platform at present, and is available only on WordPress. This CMS powers an extraordinary 33% of the internet. Its primary appeal is that the plugin itself is free and has an enormous community providing support and plugins, both free and paid. These can add huge additional functionality to the core feature-set.
WooCommerce is self-hosted, meaning you are responsible for managing your web hosting, which can be challenging for beginners who often need to learn how to diagnose and solve problems themselves. However, one advantage of self-hosting is that you own all your data, which isn’t stored on any third-party servers.
To make the process easier, services like InstaWP offer streamlined hosting solutions for WordPress, including one-click staging environments. This allows you to test changes, plugins, or themes without affecting your live site, making it an ideal choice for those new to WooCommerce or WordPress.
WooCommerce Pros
- Integrates with the most popular CMS in the world to create a seamless experience.
- Brilliant for SEO, the best platform out there in this area.
- Thousands of themes and plugins to choose from.
- Extremely customizable and has a huge ecosystem of developers.
WooCommerce Cons
- Good hosting can get expensive. See our WooCommerce hosting guide for recommendations in this area.
- No official live support. Can be challenging for store owners who need to get up to speed quickly when it comes to diagnosing issues such as plugin conflicts and security.
Magento
Firstly, there are two versions of Magento. Magento Opensource used to be called the ‘Community’ version and is free and open sourced. You can install and host this on your server and customize it as you wish. Magento Commerce is a paid version, hosted on the cloud. It includes more advanced features such as customer reward programmes, additional marketing options and targeted promotions.
This latter version starts at $22,000 a year and includes 24/7 support. Just to repeat, that’s $22,000 at a minimum. Every year.
Magento is typically the platform of choice if you have a large brand, need a solid and flexible codebase and have the turnover to justify paying such an amount. For the free Opensource version, you’ll need to have a high degree of technical expertise to install and maintain this platform, and will require powerful hosting to run it.
Magento Pros
- Trusted by large global brands such as Canon, Helly Hansen, and Burger King.
- Extremely flexible and comes with a large number of default features other platforms lack. These include the ability to manage multiple stores, prices, locations and currencies.
Magento Cons
- Requires a powerful, dedicated server to run which is expensive.
- Steep learning curve and less user friendly compared to the other options. If you want to get started quickly you’d be better looking at Shopify.
- Needs a high level of technical expertise to implement and good Magento developers don’t come cheap.
BigCommerce
BigCommerce is an interesting eCommerce platform which is gaining interest among medium-sized shops who want a professional and easy to manage store. It is an all-in-one solution so it contains everything you need to run an online shop. This includes the ability to even sell on other systems such as Ebay, Amazon and Google Shopping, all from one interface.
Like Shopify, you don’t need to worry about hosting and security. Everything is managed on BigCommerce’s own servers, and they claim an impressive 99.999% uptime rate.
BigCommerce Pros
- A dedicated eCommerce platform with a user-friendly dashboard and excellent phone support.
- No payment processing fees outside what is charged by the merchant provider. This can result in big savings for stores with a lot of orders.
- BigCommerce for WordPress version available so it can be easily integrated with the world’s most popular CMS.
- Excellent abandoned cart feature included from the Plus plan ($79.95/mo) upwards. BigCommerce claim this can recover up to 15% of orders.
BigCommerce Cons
- Pricing is based upon your store’s annual sales and you’re automatically bumped up to the next if you exceed it. The basic plan for $29.95 a month covers annual revenue of up to $50,000.
- Designers might crave more freedom when it comes to customizations.
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a way to sell products online without having to procure products, or warehouse space, or perform any of the shipping. Essentially, you create an agreement with a third-party supplier that while you accept the orders, they will do the hard work around fulfilment.
In return they will take a percentage cut out of your profit margin. The barrier for entry for dropshipping is lower than other eCommerce businesses however so for many, it’s an ideal way to introduce yourself to the industry. To learn more about this aspect of eCommerce, see our extensive WooCommerce Dropshipping Guide.
Our Shoptimizer WooCommerce theme can be used for creating a dropshipping website alongside the AliDropship plugin. Our 4.5 hour video tutorial goes through the entire process from scratch. We created a brand new site just for the experiment, selling headphones.
Fulfilment By Amazon (FBA) Services

One other option is to use the power of Amazon to do a lot of the work for you. Over two million people use Amazon to sell online by utilizing their warehouse space and rapid delivery services. It works like this:
- You send Amazon your products and they store them in their massive fulfilment centres.
- A customer buys your item. The entire transaction is seamlessly processed by Amazon, and the stock level is automatically adjusted.
- Amazon will box and deliver the product using their huge and supremely efficient worldwide postage network.
- Customer service questions and returns are dealt with by Amazon.
- You get paid every two weeks when your sales (minus seller fees) are tabulated and the amount is deposited into your bank account.
By using Amazon you don’t need to even set up a website or deal with any customer support. Your focus can be entirely on shifting product. If you have a physical product to sell and are unsure about potential demand this can be an ideal way to test the waters. It keeps your initial costs (and focus) on your products without having to worry about creating any eCommerce infrastructure, by offloading this to Amazon.
Did I miss anything?
Now, I’d like to hear from you. Which of the eCommerce options listed above was your favourite? Or maybe I missed a great eCommerce platform which should have been included. Either way, let me know by leaving a comment below right now.